The Evolution Of The Home Phonograph: A Journey Of Sound Recording And Playback
The Evolution of the Home Phonograph: A Journey of Sound Recording and Playback
Related Articles: The Evolution of the Home Phonograph: A Journey of Sound Recording and Playback
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Evolution of the Home Phonograph: A Journey of Sound Recording and Playback. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Evolution of the Home Phonograph: A Journey of Sound Recording and Playback
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/phonograph-cornet-3000-3x2gty-5a44fb749802070037ea6de4.jpg)
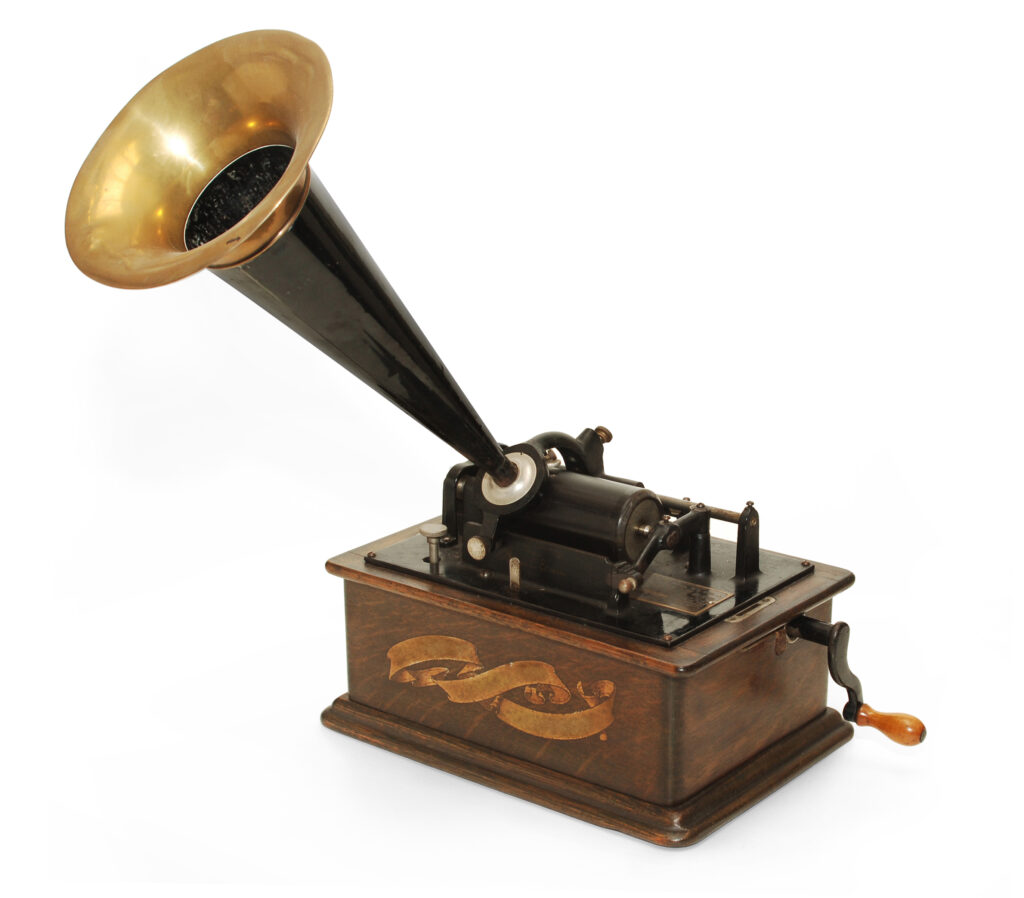
The home phonograph, a device that brought the magic of recorded music into the everyday lives of millions, has a rich and fascinating history. This journey began in the late 19th century with the invention of the phonograph, a device that allowed for the recording and playback of sound. While initially used for entertainment and novelty, the phonograph quickly evolved into a ubiquitous household fixture, transforming the way people consumed music and entertainment.
The Birth of Sound Recording: From Edison’s Vision to the First Home Phonographs
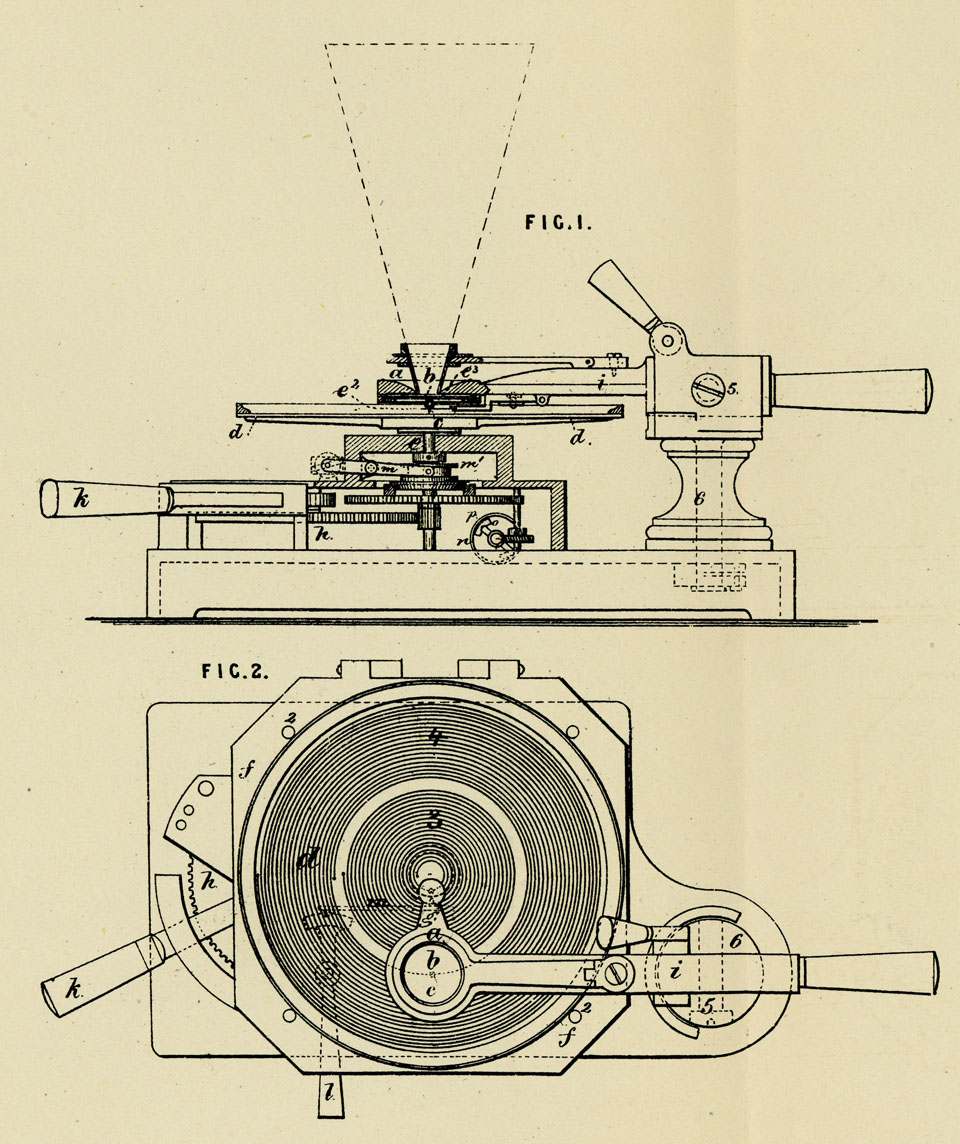
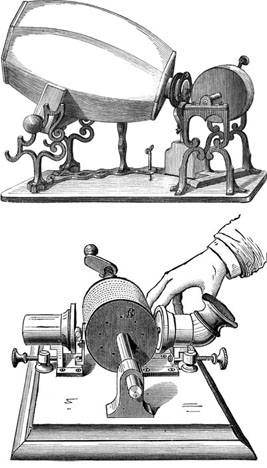
The story of the home phonograph begins with Thomas Edison, who in 1877, patented the first practical phonograph. This early device utilized a tinfoil cylinder to record sound vibrations, which were then reproduced by a needle tracing the grooves etched on the cylinder. While Edison envisioned the phonograph for dictation and communication, its potential for entertainment quickly became apparent.
The early phonographs were bulky and expensive, primarily used in public demonstrations and performances. However, the allure of bringing recorded music into the home spurred innovation. In the 1890s, Emile Berliner introduced the gramophone, a device that used flat, disc-shaped records made of shellac. The gramophone was smaller, more affordable, and offered better sound quality than the cylinder phonographs. This innovation paved the way for the widespread adoption of phonographs in homes.
The Golden Age of the Phonograph: Technological Advancements and Cultural Impact
The early 20th century marked the golden age of the phonograph. Technological advancements led to improvements in sound quality, durability, and affordability. The introduction of the electric phonograph in the 1920s further revolutionized the industry, eliminating the need for winding up the mechanism. This made phonographs more accessible and user-friendly, solidifying their place in homes around the world.
The phonograph’s cultural impact was immense. It democratized access to music, allowing people to enjoy their favorite artists and genres in their own homes. The development of the record industry, driven by the popularity of the phonograph, led to the rise of major music labels and the creation of a global music market.
The Rise of Radio and the Continued Evolution of the Phonograph
The advent of radio in the 1920s posed a significant challenge to the phonograph. Radio offered free, live entertainment, directly competing with the phonograph’s pre-recorded music. However, the phonograph was able to adapt and thrive, evolving to meet the changing needs of consumers.
The development of the long-playing (LP) record in the 1940s provided a significant leap forward. LPs offered longer playing times and improved fidelity, making them a preferred choice for classical music and more complex genres. The introduction of stereo sound in the 1950s further enhanced the listening experience, offering a more immersive and realistic sound.
The Digital Revolution and the Legacy of the Home Phonograph
The late 20th century witnessed the rise of digital technology, which fundamentally changed the way music was recorded, distributed, and consumed. The introduction of the compact disc (CD) in the 1980s, followed by the rise of digital music players and streaming services, marked a shift away from physical media.
While the home phonograph’s reign as the dominant music playback device came to an end, its legacy remains significant. The phonograph’s impact on music, entertainment, and culture is undeniable. It played a pivotal role in the development of the music industry, democratized access to music, and fostered a global culture of music appreciation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the History of the Home Phonograph
Q1: What was the main purpose of the first phonographs?
A1: While Thomas Edison envisioned the phonograph primarily for dictation and communication, its entertainment potential quickly became apparent. Early phonographs were used for public demonstrations and performances, showcasing the novelty of recorded sound.
Q2: What were the key technological advancements that made phonographs more accessible to the public?
A2: The development of the gramophone by Emile Berliner, which used flat, disc-shaped records, made phonographs smaller, more affordable, and offered better sound quality. The introduction of the electric phonograph in the 1920s further simplified the process, eliminating the need for winding up the mechanism.
Q3: How did the phonograph influence the music industry?
A3: The phonograph’s popularity led to the rise of the record industry, with major music labels emerging to produce and distribute records. This created a global music market, fostering the creation and consumption of music on an unprecedented scale.
Q4: How did the phonograph adapt to the rise of radio?
A4: The phonograph responded to the challenge of radio by evolving its technology. The development of the long-playing (LP) record in the 1940s offered longer playing times and improved fidelity, catering to a broader range of musical genres. The introduction of stereo sound in the 1950s further enhanced the listening experience, providing a more immersive and realistic sound.
Q5: What is the legacy of the home phonograph?
A5: The home phonograph’s legacy is profound. It played a crucial role in the development of the music industry, democratized access to music, and fostered a global culture of music appreciation. Its impact on entertainment and culture is undeniable, shaping the way people consume music and entertainment to this day.
Tips for Understanding the History of the Home Phonograph
- Explore museum collections: Many museums dedicated to music, technology, or history house collections of early phonographs and records. Visiting these museums can provide a hands-on experience with the evolution of the technology.
- Read historical accounts: Numerous books and articles delve into the history of the phonograph and its impact on society. These resources provide detailed insights into the technological advancements, cultural significance, and influential figures associated with the phonograph.
- Listen to early recordings: Accessing recordings from the early days of the phonograph allows for a deeper understanding of the sound quality and artistic expression of the era. Online archives and historical record collections offer a wealth of material to explore.
- Engage in discussions: Participating in online forums or discussions focused on music history or vintage technology can provide valuable insights and perspectives from fellow enthusiasts.
Conclusion
The home phonograph, from its humble beginnings as a novelty device to its evolution into a cornerstone of home entertainment, has left an indelible mark on history. It revolutionized the way people consumed music, fostered the development of the music industry, and played a significant role in shaping the cultural landscape of the 20th century. While the digital revolution has brought about a new era of music consumption, the home phonograph’s legacy continues to inspire and remind us of the transformative power of sound recording and playback.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Evolution of the Home Phonograph: A Journey of Sound Recording and Playback. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!